Expert Insights: The Role of Nutrition in Mental Health
The Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health
In recent years, the understanding of mental health has expanded beyond traditional psychological theories and practices. One area that has gained significant attention is the impact of nutrition on mental well-being. Experts have increasingly recognized that what we eat can profoundly influence our mental health, affecting everything from mood to cognitive function.

The Science Behind Nutrition and Mental Health
Scientific research has established a strong link between diet and mental health. The brain, like any other organ, requires a variety of nutrients to function optimally. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, are known to support brain health and may reduce symptoms of depression. Similarly, vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, and zinc play crucial roles in neurotransmitter function and mood regulation.
Studies have shown that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins are associated with a lower risk of depression and anxiety. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can have a negative impact on mental health.
Gut Health: The Second Brain
The concept of the gut-brain axis has revolutionized our understanding of the connection between diet and mental health. The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of bacteria, plays a critical role in producing neurotransmitters such as serotonin, often referred to as the "feel-good" hormone. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammation and has been associated with mental health disorders.

Consuming probiotics and prebiotics through foods like yogurt, kefir, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. This not only supports digestive health but also promotes mental well-being.
The Role of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are another important component in the diet that can impact mental health. They help combat oxidative stress in the brain, which is linked to neurodegenerative diseases and mood disorders. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries, nuts, and leafy greens.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help protect your brain from damage and support overall mental health.

Practical Tips for a Mental Health-Friendly Diet
Adopting a diet that supports mental health doesn't have to be complicated. Here are some practical tips:
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals.
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains.
- Incorporate sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Limit intake of processed foods and sugars.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
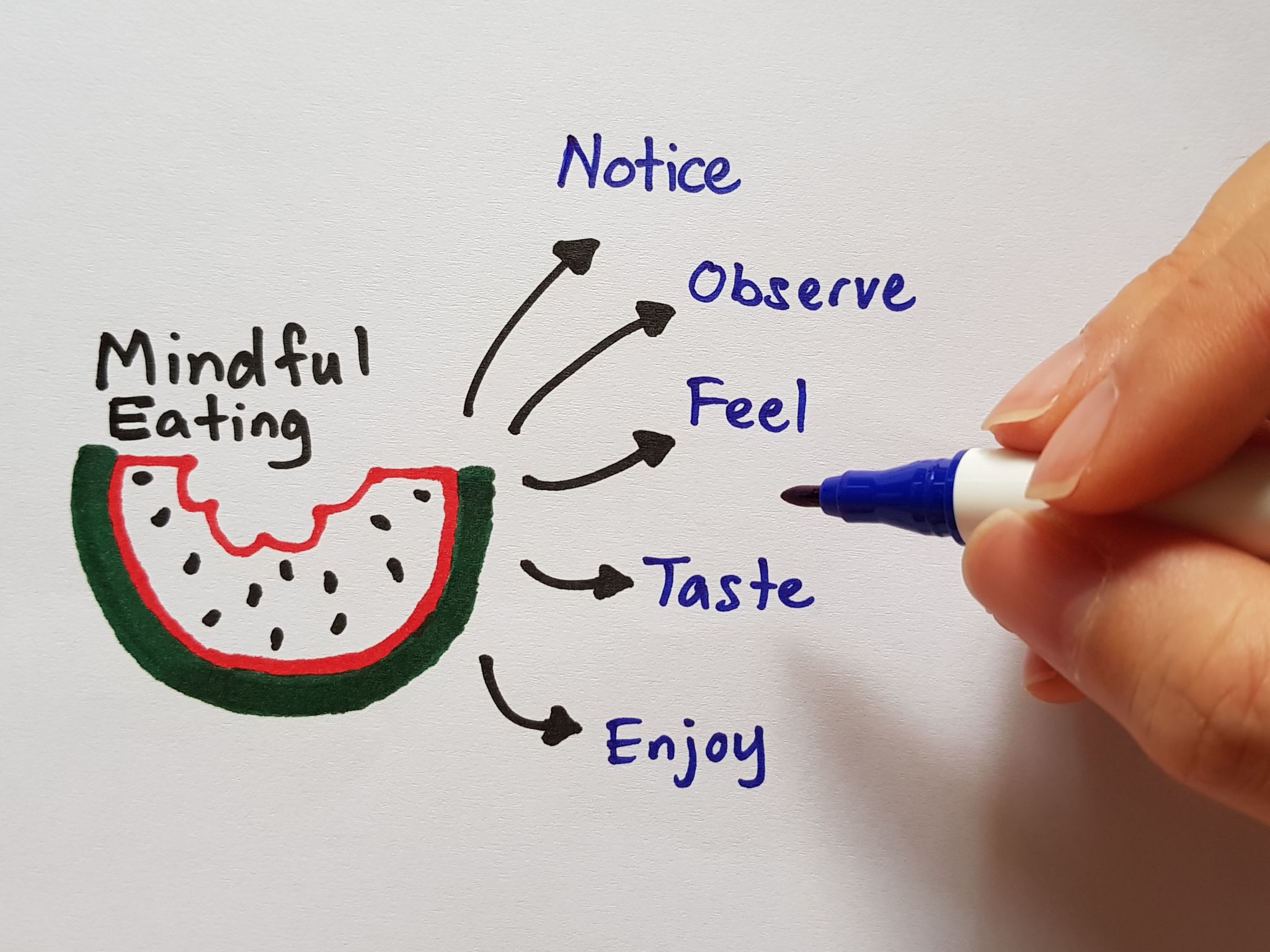
The Benefits of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is another approach that can enhance the relationship between diet and mental health. It involves paying attention to the taste, texture, and sensations of food, leading to better digestion and a more satisfying eating experience. Mindful eating encourages individuals to listen to their body's hunger cues and make more conscious food choices.
Conclusion
The relationship between nutrition and mental health is complex but undeniable. By understanding the impact of diet on our mental well-being, we can take proactive steps to improve our mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance cognitive function. As research continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly clear that nutrition should be an integral part of any comprehensive approach to mental health care.
